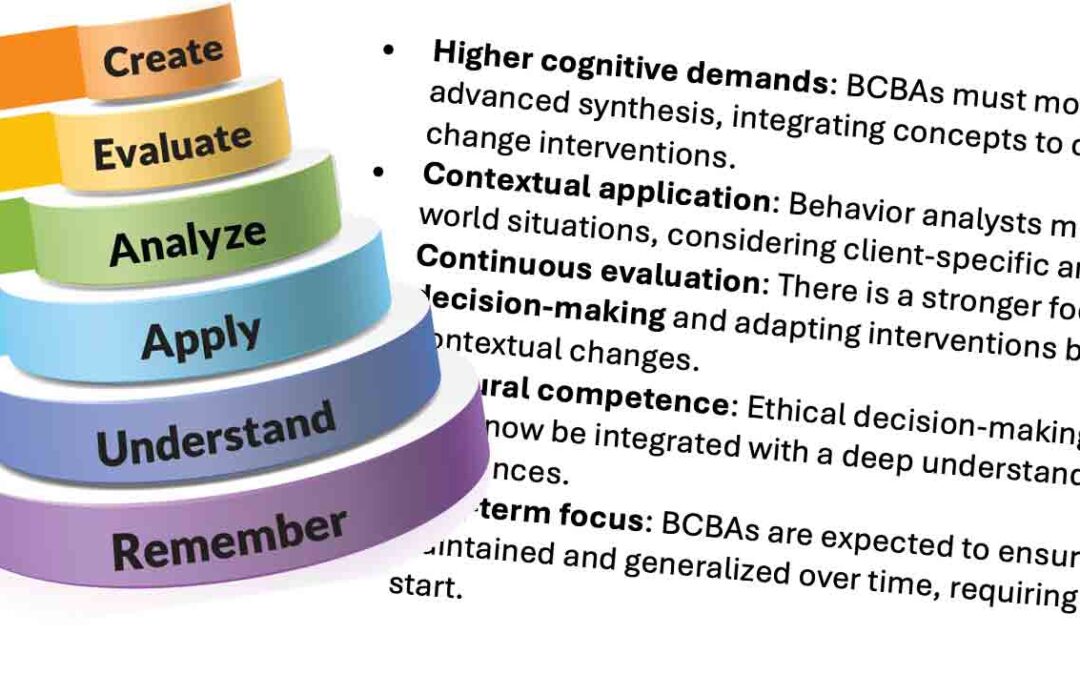
The escape condition is conducted to determine if the function of the behavior is escape. The condition is conducted as follows:
- Non-preferred demands place on client to establish MO
- If there is no response or an incorrect response, the correct response is provided
- If a problem behavior occurs, the demand is removed and the client is told something like “That’s OK, we don’t have to do that right now.”.
- The demand is reintroduced after a few minutes.
- The process is repeated.
If the problem behavior is highest in this condition, the function is escape.